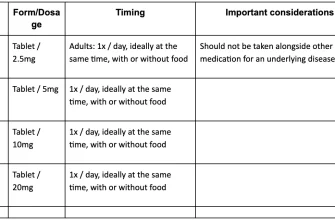
Need clear information about the link between Naion (non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy) and Cialis? Focus on this: men with certain risk factors for Naion should discuss Cialis use with their doctor before starting treatment. This includes those with a history of cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes – conditions that already compromise blood flow. Ignoring this advice could lead to serious vision problems.
Cialis, like other phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors, works by increasing blood flow. While beneficial for erectile dysfunction, this increased blood flow can sometimes affect the optic nerve, potentially causing Naion. This risk is generally low, but it’s crucial to be aware. The increased blood flow isn’t always a direct cause; it’s more accurate to say that pre-existing conditions leading to compromised blood flow are exacerbated. Therefore, open communication with your physician is paramount.
Specific actions to take: Provide your doctor with a complete medical history, including any eye conditions. Discuss your lifestyle factors such as smoking, diet and exercise, as these can impact blood flow and thus the risk of Naion. Regular eye exams are also recommended, particularly if you’re taking Cialis or other PDE5 inhibitors. Early detection of any vision changes is key to prompt management.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes and should not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication, especially if you have concerns about Naion.
- Naion and Cialis: Understanding the Risk
- Identifying Risk Factors
- Minimizing Risk
- Alternative Treatments
- Understanding Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION)
- Symptoms of NAION
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Cialis and its Potential Link to NAION
- Risk Factors and Mitigation Strategies
- Age and Pre-existing Conditions
- Medication Interactions
- Lifestyle Choices
- Monitoring and Early Intervention
- Specific Risk Reduction
- Individualized Approach
- Seeking Medical Advice and Treatment Options
- Diagnosis
- Treatment Options
- Post-Treatment Care
- Finding a Specialist
- Important Considerations
- Additional Resources
Naion and Cialis: Understanding the Risk
Cialis, like other phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors, carries a small but real risk of causing Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION). NAION is a condition that can lead to sudden vision loss. This risk is heightened in individuals already predisposed to NAION, such as those with certain risk factors.
Identifying Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of NAION after using Cialis. These include age (over 50), high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and a history of heart disease. Men with pre-existing optic nerve problems are also at increased risk. Understanding your personal risk profile is paramount.
Minimizing Risk
Open communication with your doctor is crucial. Discuss your medical history, including any eye conditions or cardiovascular issues, before starting Cialis or similar medications. Regular eye exams are recommended, particularly if you experience any sudden vision changes. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle–including managing blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels–can also reduce your risk. Your doctor can provide personalized advice based on your individual circumstances. If you experience sudden vision loss after taking Cialis, seek immediate medical attention.
Alternative Treatments
If you’re concerned about the NAION risk associated with Cialis, your doctor can discuss alternative treatments for erectile dysfunction. Numerous options exist, and they can help you find a suitable solution that aligns with your health profile and minimizes potential risks.
Understanding Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION)
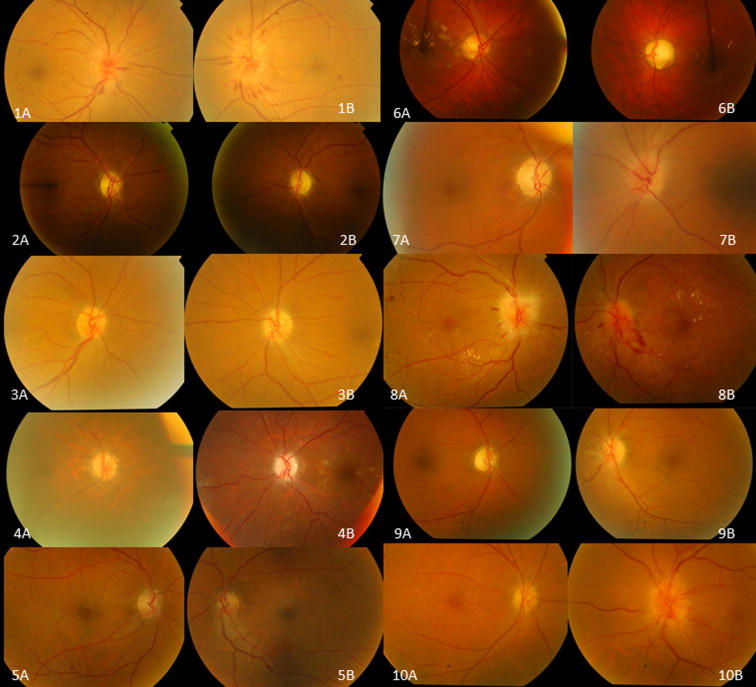
NAION is a sudden loss of vision caused by reduced blood flow to the optic nerve. This typically affects one eye, resulting in blurry vision, loss of central vision, or a blind spot. Risk factors include high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea. Men over 50 are more commonly affected. Early diagnosis is key to managing the condition.
Symptoms of NAION
Symptoms usually appear suddenly. You might notice blurry vision, a blind spot in your central vision, or decreased visual acuity. Pain is uncommon, unlike in arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AAION). These symptoms warrant immediate attention from an ophthalmologist. A thorough eye exam is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Be aware of any sudden vision changes and seek medical help promptly.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive ophthalmological examination including visual acuity tests, visual field tests, and optic nerve imaging (optical coherence tomography or OCT). Treatment focuses on managing underlying risk factors and may include medications to improve blood flow. Unfortunately, there is no proven treatment to directly reverse vision loss from NAION. However, managing risk factors can help prevent future episodes and protect the remaining vision in the affected eye.
Cialis and its Potential Link to NAION
Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) is a serious eye condition that can cause vision loss. Studies suggest a possible association between NAION and the use of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors, like Cialis. This link isn’t fully understood, but research indicates a potential increased risk, particularly in individuals with pre-existing risk factors.
Men with NAION risk factors should discuss Cialis use with their doctor. These factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and age over 50. Open communication is key to managing potential risks.
While some studies show a correlation, it’s crucial to remember that correlation doesn’t equal causation. More research is needed to definitively establish a causal relationship. However, informed consent is vital; your physician can help assess your personal risk profile and weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks of Cialis.
If you experience sudden vision loss, seek immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preserving vision. This includes a thorough eye exam to determine the cause of vision loss.
Always follow your doctor’s prescription instructions precisely. They can provide tailored advice based on your individual health and medical history. Regular eye exams, even without Cialis use, are recommended for men over 50 or those with risk factors for NAION.
Risk Factors and Mitigation Strategies
Consult your doctor before starting Cialis, especially if you have a history of heart problems or high blood pressure. Regular checkups are key to preventing complications.
Age and Pre-existing Conditions
Men over 50, those with diabetes, high cholesterol, or a history of cardiovascular disease face a higher risk of NAION. Maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels through diet and exercise is crucial.
Medication Interactions
Certain medications can increase your risk. Discuss all your current medications with your doctor, including over-the-counter drugs, before starting Cialis. This open communication is paramount.
Lifestyle Choices
Smoking significantly elevates your risk. Quitting smoking improves your overall health and reduces your chances of experiencing NAION. Regular moderate exercise and a balanced diet also contribute positively.
Monitoring and Early Intervention
Be aware of sudden vision loss symptoms. Immediate medical attention is critical if you experience any vision changes. Prompt diagnosis and treatment may improve outcomes.
Specific Risk Reduction
| Risk Factor | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure | Regular blood pressure monitoring and medication adherence as prescribed. |
| High Cholesterol | Dietary changes, exercise, and medication if needed. |
| Diabetes | Strict blood sugar control through diet, exercise, and medication. |
| Smoking | Cessation programs and support groups. |
Individualized Approach
Your doctor will assess your specific risk factors and recommend the best course of action. Open communication with your healthcare provider is vital for personalized care.
Seeking Medical Advice and Treatment Options
Contact your ophthalmologist immediately if you experience sudden vision loss. This is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will conduct a thorough eye exam, including visual acuity tests, visual field tests, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans. They may also order other tests to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment aims to improve blood flow to the optic nerve. Options include:
- Medication: Some medications can help lower blood pressure and improve blood flow. Your doctor will determine the appropriate medication based on your individual health profile.
- Intraocular Pressure Management: If elevated intraocular pressure is a contributing factor, medication or surgery might be used to lower it.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol, can significantly improve outcomes.
Post-Treatment Care
Following treatment, regular monitoring of your vision is necessary. Your doctor will provide specific instructions and schedule follow-up appointments.
Finding a Specialist
If you need a specialist, consult your primary care physician for a referral to a retinal specialist or ophthalmologist experienced in treating NAION.
Important Considerations
- Early diagnosis is key to maximizing positive outcomes.
- Treatment success varies depending on the severity and individual factors.
- Complete recovery is not always guaranteed, but effective treatment can help minimize vision loss.
Additional Resources
The American Academy of Ophthalmology website provides reliable information about NAION and its management. Always verify information with your healthcare provider.