Seek professional medical advice before starting any treatment, including Cialis. This article provides information on female Cialis trials, but it’s not a substitute for a doctor’s consultation.
Several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy and safety of tadalafil (Cialis) for women experiencing various sexual dysfunctions. Results suggest potential benefits in improving certain aspects of sexual function, particularly desire and arousal, though more research is needed to fully understand the effects and identify appropriate patient populations. Specifically, studies have focused on women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD), analyzing changes in sexual desire, arousal, and satisfaction levels after treatment.
Data from these trials often highlights variations in responses amongst participants. Factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of co-morbid conditions play significant roles in treatment outcomes. Consequently, individualized assessment is critical before prescribing tadalafil off-label for female sexual dysfunction. Doctors should carefully consider individual patient characteristics and conduct a thorough risk-benefit analysis.
Remember: This information aims to provide a concise summary; always consult medical literature for detailed findings and interpretations from the specific clinical trials. Reliable sources include peer-reviewed journals and reputable medical organizations.
- Female Cialis Trial: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding the Physiology of Female Sexual Dysfunction
- The Role of Neurotransmitters
- Psychological and Relational Influences
- Cialis’s Mechanism of Action in Women: What the Trials Show
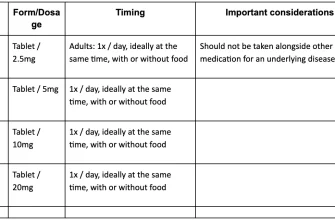
- Dosage and Response
- Side Effects and Contraindications
- Efficacy and Safety Profile: Weighing the Benefits and Risks
- Dosage and Response
- Side Effects: A Realistic Perspective
- Individualized Approach
- Conclusion: Informed Decision-Making
- Future Directions and Unanswered Questions in Research
- Investigating Underlying Mechanisms
- Long-Term Effects and Safety
- Exploring Different Formulations and Dosage
- Addressing Patient Preferences and Barriers
- Comparative Effectiveness Research
Female Cialis Trial: A Detailed Overview
Focus on understanding the specific trial you’re interested in. Each trial has unique inclusion/exclusion criteria, dosage regimens, and primary endpoints. Consult clinical trial registries like ClinicalTrials.gov for precise details.
Expect a thorough medical evaluation before enrollment. This typically includes a complete medical history, physical examination, and potentially blood tests. Be prepared to discuss your sexual health history openly and honestly with your doctor.
Trial participation involves regular visits to the study site. Frequency varies, but expect multiple appointments for monitoring and assessment. Adherence to the prescribed medication schedule is crucial.
Data collected commonly includes:
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Sexual Function Questionnaires | Standardized surveys measuring various aspects of sexual function. |
| Physical Examinations | Regular check-ups to monitor overall health and potential side effects. |
| Blood Tests | To assess liver and kidney function, as well as other relevant biomarkers. |
| Adverse Event Reporting | Detailed reporting of any side effects experienced during the trial. |
Potential side effects can vary. Common ones might include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, or digestive upset. Report all side effects immediately to the study staff.
Understand that participation is voluntary. You have the right to withdraw from the trial at any time without penalty. Your privacy will be protected according to ethical guidelines and regulations.
Results are usually presented at medical conferences and published in peer-reviewed journals. Access to individual participant data is generally restricted; however, summary findings will often be available.
Always discuss trial participation with your healthcare provider to determine its suitability for your individual circumstances and health profile.
Understanding the Physiology of Female Sexual Dysfunction
Female sexual dysfunction stems from a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and relational factors. Hormonal imbalances, notably decreased estrogen levels after menopause or due to certain medical conditions, significantly impact libido and vaginal lubrication. Reduced blood flow to the genitals, influenced by vascular disease or certain medications, contributes to arousal difficulties. Neurological conditions affecting nerve function can also impair sensation and responsiveness.
The Role of Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin play crucial roles in sexual desire and response. Imbalances in these neurotransmitter systems, often influenced by stress, anxiety, or depression, can disrupt the normal physiological processes involved in sexual arousal and satisfaction. For example, low dopamine levels are associated with reduced libido. Effective treatment strategies often address these underlying neurochemical factors.
Psychological and Relational Influences
Beyond the physiological, psychological factors like stress, anxiety, and relationship issues heavily influence sexual function. Body image concerns, past trauma, and communication problems with partners all contribute to sexual dysfunction. Addressing these issues through therapy or counseling is often a critical component of successful treatment.
Cialis’s Mechanism of Action in Women: What the Trials Show
Limited research exists on Cialis’s effects specifically in women. Existing studies primarily focus on its efficacy in treating symptoms related to the female sexual dysfunction. These trials suggest Cialis acts by increasing blood flow to the clitoris and pelvic region, potentially improving arousal and lubrication. The mechanism isn’t fully understood, but it likely involves interactions with nitric oxide pathways similar to its action in men, although perhaps with a different balance of affected pathways. The clinical trials haven’t shown consistent, strong effects across all women.
Dosage and Response
Studies have explored various dosages, revealing that responses vary considerably among participants. Some women experience improvements in sexual function with lower doses; others require higher doses or find the medication ineffective. Individual responses, therefore, are critical to consider. More research is needed to refine optimal dosage strategies for women.
Side Effects and Contraindications
Reported side effects in women are generally similar to those seen in men, including headache, flushing, and nasal congestion. However, frequency and severity can vary significantly. Women with certain cardiovascular conditions or taking specific medications should carefully discuss potential interactions with their healthcare providers before using Cialis. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are definite contraindications.
Efficacy and Safety Profile: Weighing the Benefits and Risks
Tadalafil, the active ingredient in Cialis, demonstrates efficacy in improving sexual function in premenopausal women with acquired hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD). Studies show statistically significant improvements in sexual desire, arousal, and satisfaction compared to placebo. However, response varies; not all women experience significant benefit.
Dosage and Response
Typical dosages are investigated, with results suggesting a positive correlation between dosage and improvement in certain symptoms. However, higher dosages don’t guarantee better results and may increase the likelihood of side effects. Doctors tailor treatment plans to individual needs and responses.
Side Effects: A Realistic Perspective
Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and dyspepsia. These are generally mild and transient. Rare but more serious side effects, such as vision changes or hearing loss, require immediate medical attention. Open communication with your doctor is vital for managing any side effects.
Individualized Approach
The decision to use tadalafil for HSDD should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. They will consider your medical history, other medications you take, and potential risks before prescribing. Regular monitoring is recommended to assess efficacy and manage any side effects.
Conclusion: Informed Decision-Making
Balancing potential benefits with potential risks is crucial. While tadalafil shows promise in treating HSDD in some women, it’s not a guaranteed solution for everyone. A thoughtful conversation with your physician ensures you make the most informed decision for your individual circumstances.
Future Directions and Unanswered Questions in Research
Larger, more diverse clinical trials are needed to solidify current findings and explore Cialis’s efficacy across a wider range of female sexual dysfunction presentations. We must specifically focus on subgroups defined by age, underlying medical conditions, and sexual history.
Investigating Underlying Mechanisms
Further research should explore the precise mechanisms by which Cialis affects female sexual function. This includes investigating its interaction with various neurotransmitters and hormonal pathways, potentially leading to the development of more targeted therapies.
- Studies should investigate the role of nitric oxide and its downstream effects.
- Research should also explore potential interactions with other medications commonly used in women’s health.
Long-Term Effects and Safety
Longitudinal studies are necessary to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of Cialis for treating female sexual dysfunction. This includes monitoring for potential side effects over extended periods and evaluating sustained improvements in sexual function.
- Studies should track both physical and psychological aspects of sexual health.
- Researchers should focus on identifying potential risk factors for adverse events.
Exploring Different Formulations and Dosage
Investigating alternative formulations, such as topical applications or different dosage regimens, may improve efficacy and reduce potential side effects. This could lead to more personalized treatment options.
- Explore the potential benefits of lower doses or intermittent use.
- Develop alternative routes of administration to enhance patient compliance and reduce systemic effects.
Addressing Patient Preferences and Barriers
Qualitative research is crucial to understand patient perspectives on Cialis’s use for female sexual dysfunction. This includes assessing patient preferences, identifying barriers to treatment, and improving patient education and communication strategies. Addressing these elements is key to ensuring that any discovered therapies reach those who need them.
Comparative Effectiveness Research
Direct comparisons between Cialis and other treatments for female sexual dysfunction are needed to determine its relative advantages and disadvantages. This head-to-head research can guide clinicians in making informed treatment decisions.