Need quick, reliable information on Cialis? Consult Medscape’s drug reference for detailed prescribing information, including dosage, contraindications, and potential side effects. This resource provides a clear, concise overview of the medication’s clinical profile.
Medscape offers access to clinical trial data and a wealth of peer-reviewed articles directly relevant to Cialis’s use and efficacy. This allows for a thorough understanding of its applications and potential limitations. Look for specific information related to your patient’s individual needs.
Remember to always verify information with your own research and consult your medical resources. Proper patient assessment and careful consideration of individual medical histories are paramount before prescribing Cialis or any medication. Medscape serves as a valuable tool, but not a replacement for professional clinical judgment.
Note: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
- Cialis (Tadalafil) Information from Medscape
- Dosage and Administration
- Important Safety Information
- Contraindications
- Mechanism of Action and Pharmacokinetics
- Approved Indications and Uses
- Beyond Erectile Dysfunction
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Dosage Adjustments
- Common Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Alpha-Blockers and Blood Pressure
- Other Notable Interactions
- Contraindications: When to Avoid Cialis
- Monitoring Parameters and Patient Counseling
- Clinical Considerations and Special Populations
- Cardiac Considerations
- Specific Patient Groups
- Drug Interactions
- Monitoring
- Dosage Adjustment
- Further Information
Cialis (Tadalafil) Information from Medscape
Medscape provides detailed prescribing information for Cialis (Tadalafil), including indications, dosages, and warnings. Consult Medscape for the most current and complete data, as drug information changes.
Dosage and Administration
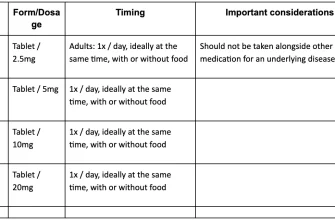
Typical dosages for erectile dysfunction range from 5mg to 20mg, taken as needed, at least 30 minutes before sexual activity. For benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), the usual dose is 5mg once daily. Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on individual patient response and tolerance. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Important Safety Information
Cialis can interact with nitrates, potentially causing a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Patients with heart problems should exercise caution. Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and dyspepsia. Serious but rare side effects exist; prompt medical attention is necessary for prolonged erection (priapism) or sudden vision loss. Medscape’s drug information offers a full list of potential interactions and adverse reactions.
Contraindications
Cialis is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to tadalafil or its components. It should be avoided in individuals with certain cardiovascular conditions. Consult Medscape for a complete list of contraindications.
Mechanism of Action and Pharmacokinetics
Cialis, or tadalafil, works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), an enzyme that breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Increased cGMP levels relax smooth muscle in the corpus cavernosum, allowing increased blood flow and facilitating erection.
Pharmacokinetic properties are key to understanding Cialis’s effectiveness and duration of action:
- Absorption: Tadalafil is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations typically achieved within 2 hours.
- Distribution: It’s extensively distributed throughout the body, with a high volume of distribution.
- Metabolism: Primarily metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. This is important to consider when co-administering with other medications metabolized by this enzyme.
- Excretion: Eliminated mainly through feces (approximately 61%) and urine (approximately 36%).
- Half-life: Has a long elimination half-life, around 17.5 hours, contributing to its extended duration of action.
Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on renal or hepatic impairment. For example, lower doses might be recommended for patients with severe kidney disease. Always consult prescribing information for specific recommendations.
Food slightly reduces the rate of absorption but not the extent; therefore, it can be taken with or without food.
- Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Approved Indications and Uses
Cialis (tadalafil) receives FDA approval primarily for treating erectile dysfunction (ED) in adult men. This means it helps men achieve and maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
Beyond Erectile Dysfunction
Cialis also holds approval for treating the signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition causing an enlarged prostate. This approval is for men experiencing both ED and BPH symptoms. Importantly, Cialis can help alleviate urinary symptoms associated with BPH, such as frequent urination or weak urinary stream. It’s crucial to note that Cialis treats the symptoms, not the underlying cause of BPH.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is another approved indication. In this case, Cialis is prescribed to improve exercise capacity in adults with this specific type of high blood pressure affecting the arteries in the lungs. This use requires careful monitoring and precise dosage adjustments by a medical professional.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Cialis is typically administered orally as needed, 30 minutes to 12 hours before anticipated sexual activity. The recommended starting dose is 10 mg. However, your doctor may adjust this based on your individual needs and response to treatment.
Dosage Adjustments
For some men, a 5 mg dose may be sufficient. Others may require a higher dose of 20 mg. The maximum recommended daily dose is 20 mg. Don’t exceed this without consulting your physician.
Dosage adjustments are also needed for certain medical conditions. For example, individuals with moderate hepatic impairment should usually start with a lower dose (5 mg). Similarly, those with severe renal impairment may require dose adjustment. Always discuss your specific health conditions with your doctor before starting Cialis treatment.
Remember to take Cialis exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Follow their instructions carefully. Improper use can lead to side effects or ineffective treatment. Regularly scheduled follow-up appointments will allow your doctor to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Common Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Cialis, like most medications, can cause side effects. The most common are headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and indigestion. These usually are mild and temporary.
More serious, though less frequent, side effects include changes in vision, such as blurred vision or temporary blue-tinged vision. These visual disturbances typically resolve quickly. If you experience sudden vision loss, seek immediate medical attention.
Prolonged erection (priapism) is a rare but serious side effect requiring immediate medical help. This condition can cause permanent damage if untreated.
Hearing loss or tinnitus (ringing in the ears) are also possible, albeit uncommon, side effects. Contact your doctor if you notice any changes in your hearing.
Muscle aches and back pain can occur. These are usually manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers. However, consult your physician if pain is severe or persistent.
Allergic reactions, while infrequent, can manifest as skin rash, itching, or swelling. If you experience an allergic reaction, discontinue use and seek medical advice immediately.
This information does not cover all possible side effects. Consult the complete patient information leaflet or your doctor for a full list and to discuss any concerns.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and recreational drugs. This includes nitrates in any form, as combining them with Cialis can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. This risk extends to medications containing nitrates, such as nitroglycerin used for chest pain.
Alpha-Blockers and Blood Pressure
Cialis can interact with alpha-blockers, medications used to treat high blood pressure and enlarged prostate. Combining these can significantly lower blood pressure, potentially leading to dizziness or fainting. Your doctor should carefully monitor your blood pressure if you take both.
Other Notable Interactions
Certain antifungal medications like ketoconazole and itraconazole can increase Cialis levels in your blood, potentially intensifying side effects. Similarly, some HIV protease inhibitors may have the same effect. Discuss these interactions with your physician before using Cialis concurrently.
Contraindications: When to Avoid Cialis
Avoid Cialis if you have a history of heart problems, including recent heart attack or stroke. Severe liver or kidney disease also necessitates caution or avoidance. If you experience a sudden loss of vision, stop taking Cialis immediately and contact your doctor. Individuals with a known allergy to tadalafil (the active ingredient in Cialis) should absolutely not use the drug. Always prioritize open communication with your healthcare provider to ensure safe medication use.
Monitoring Parameters and Patient Counseling
Regularly monitor blood pressure, especially during the initial treatment phase. A significant drop in blood pressure may necessitate dose adjustment.
Assess for the presence of symptoms suggestive of myocardial ischemia, such as chest pain or discomfort. Report any such occurrences immediately.
Check for visual disturbances, including sudden vision loss. This is a rare but serious side effect requiring prompt medical attention.
Inquire about hearing changes, particularly tinnitus or sudden hearing loss. These are also rare side effects, but warrant immediate action.
Counsel patients on the proper dosage and timing of Cialis administration. Emphasize taking it as prescribed.
Advise patients on potential side effects, including headache, flushing, muscle aches, and nasal congestion. Explain that these are usually mild and transient.
Inform patients about the potential interaction with nitrates and other medications. Ensure they understand the importance of disclosing all medications to their physician.
| Parameter | Monitoring Frequency | Action if Abnormal |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Pressure | Initially, frequently; then, periodically | Dose adjustment or discontinuation |
| Chest Pain | Ongoing assessment | Immediate medical attention |
| Visual Disturbances | Regular questioning | Immediate medical attention |
| Hearing Changes | Regular questioning | Immediate medical attention |
Encourage open communication. Patients should feel comfortable reporting any concerns or adverse effects.
Provide written instructions and reiterate key points verbally to ensure patient understanding.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for ongoing assessment and management.
Clinical Considerations and Special Populations
Adjust Cialis dosage based on renal and hepatic function. For patients with moderate to severe renal impairment, reduce the dose. Similarly, reduce the dose for patients with hepatic impairment.
Cardiac Considerations
Cialis can cause vasodilation; carefully monitor patients with unstable angina or uncontrolled hypertension. Avoid concomitant use with nitrates.
- Assess cardiovascular risk before initiating therapy.
- Consider pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Monitor blood pressure regularly.
Specific Patient Groups
Use caution in patients with anatomical deformation of the penis (e.g., angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie’s disease), as priapism is a potential risk. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
- Patients with bleeding disorders: Cialis may increase bleeding risk. Exercise caution.
- Older adults: Consider age-related changes in renal and hepatic function when determining dosage.
- Patients with retinitis pigmentosa: Use with caution, as visual disturbances have been reported.
Drug Interactions
Avoid concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, ritonavir) and inducers (e.g., rifampin). These medications significantly alter Cialis metabolism. Grapefruit juice should also be avoided.
Monitoring
Regularly monitor blood pressure and assess for adverse events, such as headache, flushing, and nasal congestion. Address any concerns promptly with appropriate management strategies.
Dosage Adjustment
Always refer to the prescribing information for detailed dosage adjustments based on individual patient characteristics and comorbidities.
Further Information
Consult product labeling for complete details on prescribing information and safety considerations.